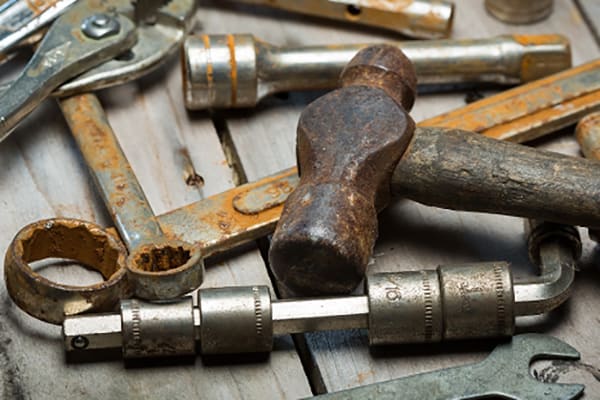
Hammers are one of the most widely used tools across various industries and households. Despite their simple design, they are subjected to heavy-duty tasks, which makes them susceptible to wear and tear. One of the significant issues faced by hammers, especially those made of steel, is corrosion. Corrosion not only diminishes the aesthetic appeal of the hammer but also reduces its durability and effectiveness. To combat this, manufacturers employ a range of anti-corrosion techniques to extend the lifespan of hammers. This article explores some of the most effective anti-corrosion methods used in hammer manufacturing.
1. Material Selection
The fight against corrosion starts at the material selection stage. Many hammers are made from high-carbon steel, which is strong but prone to rust. To mitigate this, manufacturers often choose alloy steels that contain elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. These elements enhance the steel’s resistance to corrosion. Stainless steel, for instance, is a popular choice due to its excellent anti-corrosion properties, though it is more expensive than regular carbon steel.
2. Protective Coatings
One of the most common and effective methods for preventing corrosion is applying a protective coating to the hammer. There are several types of coatings that can be used:
- Zinc Plating: This involves coating the hammer with a thin layer of zinc, which serves as a sacrificial layer that corrodes instead of the steel underneath. Zinc-plated hammers are highly resistant to rust and are often used in environments where the tool is exposed to moisture.
- Powder Coating: Powder coating is a dry finishing process where a powder (usually a thermoplastic or thermoset polymer) is applied to the hammer's surface and then cured under heat. This creates a hard, durable finish that resists corrosion and wear.
- Galvanization: This process involves dipping the hammer in molten zinc to form a thick, protective layer. Galvanized hammers are particularly effective in resisting rust and are ideal for outdoor or industrial use.
3. Oil and Wax Treatments
For hammers that need to maintain a more traditional look, especially those with wooden handles, oil and wax treatments are often used. These substances penetrate the metal’s surface and create a barrier that repels moisture and reduces the risk of corrosion. Linseed oil, beeswax, and tung oil are commonly used in these treatments. While not as robust as coatings, these treatments are easy to apply and can be re-applied periodically to maintain protection.
4. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, are not just for enhancing the hammer's strength and toughness; they can also play a role in improving corrosion resistance. By altering the microstructure of the steel, heat treatment can reduce the metal’s susceptibility to corrosion. However, this technique is often combined with other methods, like coating or material selection, for optimal results.
5. Stainless Steel Construction
For applications where corrosion resistance is paramount, stainless steel hammers are an excellent choice. Stainless steel contains a high percentage of chromium, which forms a passive layer on the metal’s surface, preventing rust from forming. Although more expensive, stainless steel hammers require minimal maintenance and are ideal for environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive substances.
6. Regular Maintenance
Beyond manufacturing techniques, regular maintenance plays a critical role in preventing hammer corrosion. Simple practices, such as wiping down the hammer after use, storing it in a dry place, and periodically applying a light coating of oil, can significantly extend the life of the tool. Users should also check for any signs of rust or wear and address them promptly to prevent further damage.
Conclusion
Corrosion is a significant challenge in maintaining the longevity and functionality of hammers, but with the right techniques, it can be effectively managed. From material selection and protective coatings to regular maintenance, there are multiple strategies that manufacturers and users can employ to protect hammers from rust and corrosion. By investing in these anti-corrosion techniques, you can ensure that your hammer remains a reliable and durable tool for years to come.
Post time: 09-10-2024